Molecules for Labeling Peripheral Nerves for use in Image Guided Surgery and Other Clinical Applications
- Technology Benefits
- • Systemic administration• Visualization in real time at the surgical field• Modular: so other dyes or molecules could be attached to targeting agent• Specific accumulation in the axonal tract of neural tissue• Potentially adaptable to delivery of neurotrophic factors to aid in repair and regeneration
- Detailed Technology Description
- Researchers at UCSD have developed a fast, targeted approach to fluorescently label nerves that addresses all the disadvantages of current techniques. A targeting element, specific for neuronal tissue, limits dye accumulation in adjacent structures. Visualization of peripheral nerves occurs within a short time frame, enabling it for practical use during surgery, and improved accumulation of the imaging agent is obtained along the axonal tract of the nerve.
- Supplementary Information
- Patent Number: US8685372B2
Application Number: US13264512A
Inventor: Tsien, Roger Y. | Nguyen, Quyen T. | Whitney, Michael
Priority Date: 15 Apr 2009
Priority Number: US8685372B2
Application Date: 29 Feb 2012
Publication Date: 1 Apr 2014
IPC Current: A61K004900 | A61K003818 | A61P002500 | C07K000708 | C07K001702 | C07K001710 | C07K001900 | G01N003353
US Class: 4240096 | 4350071 | 5140084 | 5140085 | 5140177 | 530323 | 530327 | 530399
Assignee Applicant: The Regents of the University of California
Title: Peptides and aptamers for targeting of neuron or nerves
Usefulness: Peptides and aptamers for targeting of neuron or nerves
Summary: The targeting molecule is useful for identifying neuron or nerve and delivering drug to neuron or nerve (all claimed).
Novelty: New targeting molecule, comprising a peptide or an aptamer that specifically binds to a neuron or nerve, or their component, useful for identifying neuron or nerve and delivering drug to neuron or nerve
- Industry
- Optics
- Sub Category
- Optical System
- Application No.
- 8685372
- Others
-
State Of Development
• A patent application has been filed.
• A model system has been developed and tested in mice with specific and non-specific (control) targeting componentsResults
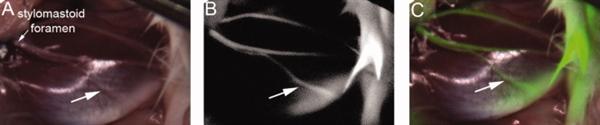
Right lateral face of a wild-type mouse treated with F-NP41. (A) White-light image of the right facial nerve. (B) Fluorescence image of the F-NP41-labeled facial nerve. (C) Composite image superimposing the fluorescence image with the white-light image. The arrows show a small nerve branch on the masseter muscle that is not clearly observed in white light (A), but becomes apparent with fluorescence (B,C).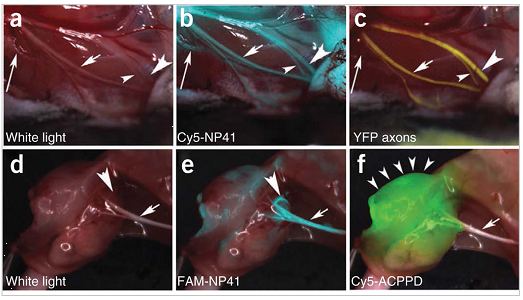
NP41 can highlight buried nerve branches invisible by standard illumination. (a–c) Right facial nerve and its arborizations in a thy1-YFP mouse treated with Cy5-NP41, viewed by (a) white light reflectance, (b) Cy5 fluorescence (pseudocolored cyan) overlaid on reflectance and (c) YFP fluorescence (pseudocolored yellow), also overlaid on reflectance. The short arrow marks a nerve branch visible by all three imaging modes. The arrowheads point to branches that are difficult to differentiate from muscle fascia in reflectance, but clearly distinguishable in both fluorescence images. The long arrow indicates a deeply buried branch visible only by Cy5-NP41 due to the better penetration of far-red wavelengths. (d–f) Left sciatic nerve (arrow) and its arborization in a mouse with a syngeneic 8119 mammary tumor graft1718, viewed by (d) white light reflectance, (e) FAM fluorescence 2 h after intravenous injection of NP41 (150 nmoles) (pseudocolored cyan, overlaid on reflectance) and (f) Cy5 fluorescence (pseudocolored green, overlaid on reflectance) from conjugates of activatable cell-penetrating peptides and dendrimers (ACPPDs). The large arrowheads in d and e point to a nerve branch buried under tumor, visible only by FAM fluorescence. Small arrowheads in f denote tumor.
Additional Technologies by these Inventors
- Proteins that Efficiently Generate Singlet Oxygen Background
- Proteins That Fluoresce At Infrared Wavelengths Or Singlet Oxygen Upon Illumination
- Dual Reflectance-Fluorescence Guided Surgical System
- Personalized Protease fingerprinting for early cancer diagnosis
Tech ID/UC Case
19289/2009-220-0
Related Cases
2009-220-0, 2013-185-0, 2013-105-0
- *Abstract
-
Surgical procedures often involve working close to vital nerve tissue and careful dissection is needed in order to preserve as much function as possible. Although some nerves are easily visualized, there are many types of procedures, such as the excision of tumors, the presence of inflammation or infection at the surgical site, scar tissue resulting from previous procedures or nerves encased in bone, where the precise location is not easily determined.
Currently nerves are typically visualized one at a time using fluorescent dyes that label nerves in either an antero- or retro-grade manner. These techniques have several drawbacks including excessively long labeling times to accumulate the imaging agent and limited accumulation of the agent along the axonal tract.
- *IP Issue Date
- Apr 1, 2014
- *Principal Investigator
-
Name: Quyen Nguyen
Department:
Name: Roger Tsien
Department:
Name: Michael Whitney
Department:
- Country/Region
- USA






