Novel Nanoliposomal Nitroglycerin Formulation for Cardiovascular Therapies
- Technology Application
- Novel formulation of NTG for potential use in conditions associated with the inflammatory process such as PAH, atherosclerosis, and diabetes A more potent formulation of NTG could be used in the current indications of chest pain and high blood pressure during surgery
- Detailed Technology Description
- None
- Application No.
- 20180177724
- Others
-
Background
Leukocyte-endothelial cell (EC) adhesion is a hallmark of the inflammatory process, and is associated with diseases such as pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), atherosclerosis, and diabetes. This adhesion is inhibited by endogenous EC-derived nitric oxide (NO), which is significantly impaired in the aforementioned conditions. Thus, NO-releasing nitrates are being investigated as anti-inflammatory therapies.
Nitroglycerin (NTG) is of particular interest among clinically-used nitrates because it spontaneously produces NO and also activates endothelial NO synthase (eNOS), the key NO-producing enzyme in ECs that is impaired in inflammatory conditions. However, NTG is not suitable for long-term clinical use due to loss of NTG sensitivity (tolerance) and endothelial dysfunction (cross-tolerance).
Related Materials
Tech ID/UC Case
28752/2016-346-0
Related Cases
2016-346-0
- *Abstract
-
To address this major limitation, investigators at UCR have developed a nanoliposomal formulation of NTG, which achieves a 70-fold increase in the anti-inflammatory effect of NTG when compared to NTG. This increase in potency allows lower doses to be effective, which could mitigate the common issues seen with high clinical doses of NTG viz. loss of NTG sensitivity and endothelial toxicity.
Fig. 1 Adhesion of U937 monocytes to NO-deficient (L-NIO-treated) ECs is significantly blocked by treating ECs with 5 ug/ml nanoliposomal nitroglycerin (NTG-NL). L-NIO is a selective eNOS inhibitor. Remarkably, this anti-inflammatory dose of NTG in nanoliposomes is 70-fold lower than the dose of free NTG (5uM) required to achieve a similar effect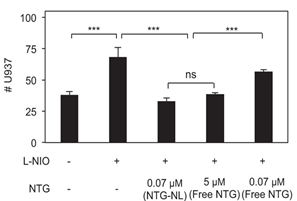
- *IP Issue Date
- Jun 28, 2018
- *Principal Investigator
-
Name: Soroush Ardekani
Department:
Name: Kaustabh Ghosh
Department:
- Country/Region
- USA






