Gold Catalyzed Hydroamination of Alkynes and Allenes
- 技术应用
- Hydroamination of alkynes and allenes Production of pharmaceuticals/bioactive molecules
- 详细技术说明
- None
- *Abstract
-
Researchers at the University of California, Riverside have developed a gold complex that functions as the catalyst used in hydroamination of alkynes and allenes. The catalyst has many forms, such as gold nanoparticles/clusters and gold compounds combined with the salts of other metals. Typically, the catalyst has the following structure: L1 – Au+ - L2. L1 and L2 are unique ligands. The catalyst is robust enough to allow hydroamination at a wide range of temperatures (0˚C - 300˚C). Depending on the starting material/catalyst used, 100% hydroamination is achieved in 6 to 24 hours.
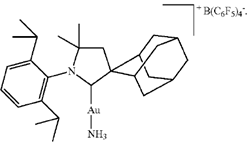
Fig. 1
One of the catalytic gold complex catalysts used for hydroamination. Note the presence of the ammonia (NH3) as one of the two ligands.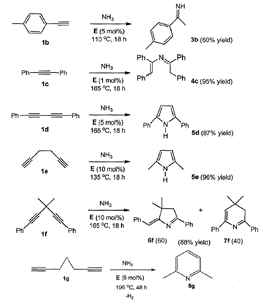
Fig. 2 Examples of catalytic amination of various alkynes with ammonia. The last four compounds are dialkynes, which contain multiple carbon-carbon double bonds. Hydroamination of these compounds leads to the formation of heterocyclic rings.
- *IP Issue Date
- Nov 12, 2013
- *Principal Investigation
-
Name: Guy Bertrand
Department:
Name: Bruno Donnadieu
Department:
Name: Guido Frey
Department:
Name: Vincent Lavallo
Department:
Name: Michele Soleilhavoup
Department:
- 申请号码
- 8580990
- 其他
-
Background
Nitrogen-carbon bonds are found in a variety of compounds, ranging from pharmaceuticals to chemical feedstocks. Specifically, the formation of C-N bonds is done via hydroamination, which adds the N-H bond of an amine group to a carbon-carbon bond via a catalyst, which is a compound that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed. This process is especially important in the synthesis of biologically active compounds.
Ammonia is among the cheapest, most readily available bulk chemicals, which has led to a widespread interest in developing techniques that can combine ammonia with organic molecules. Of particular interest is combining ammonia with multiple-bonded carbon atoms (such as those in alkynes and allenes).Related Materials
Tech ID/UC Case
29208/2008-598-0
Related Cases
2008-598-0
- 国家/地区
- 美国






