Assay for Inhibitors of Nonsense-Mediated RNA Decay
- 技术优势
- Simpler, faster, and less expensive than exogenous NMD assays Ease of use in vivo or in tissue and organs without the need to transfect reporter genes into cells.
- 技术应用
- Use of endogenous NMD assay to screen for compounds and genes that modulate PTC and/or NMD
- 详细技术说明
- None
- *Abstract
-
Prof. Sika Zheng at UCR has developed a new endogenous NMD assay that is both sensitive and quantitative. The assay can be used on its own to assess changes in cellular NMD activity with high specificity and sensitivity. It can facilitate analysis of NMD controls by cellular pathways in response to stimuli or during development and is particularly suitable for unbiased screening of NMD modulators. The assay is designed to distinguish NMD regulation from transcriptional regulation and alternative splicing control.
- *IP Issue Date
- Jan 11, 2018
- *Principal Investigation
-
Name: Sika Zheng
Department:
- 申请号码
- 20180010188
- 其他
-
Background
An estimated 9 million people in the US suffer from genetic disorders that are a consequence of a nonsense or frameshift mutation that introduces a premature termination codon (PTC). PTC is also known as a nonsense codon or premature stop codon and such codons lead to loss of protein products. Nonsense-mediated RNA decay (NMD) is a cellular quality control mechanism to selectively degrade transcripts that have a PTC codon.
Currently exogenous assays are used to screen for compounds that inhibit NMD.These labor-intensive exogenous assays use PTC-containing reporter genes and are restricted to certain transfectable cells. Since these reporter genes may not transfect the entire cell population in an assay, exogenous assays have limited sensitivity. Exogenous reporters also have a high false positive rate, because these assays are simultaneously affected by non-NMD regulation. Thus new and effective assays to screen for NMD inhibitors are desirable.
Images
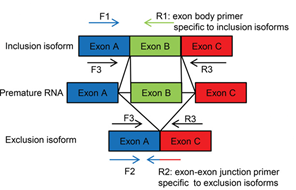
Fig. 1 shows the schematics of the novel endogenous assay that uses RT-qPCR methods to detect NMD and non-NMD isoform of the same gene. The NMD isoform can be the inclusion or the exclusion isoforms. The inclusion isoform is detected by primer F1 and isoform specific primer R1. The exclusion isoform is detected by F2 and isoform-specific junction primer R2. Primers F3 and R3 are commonly used in alternative splicing assays to detect both inclusion and exclusion isoforms.
Related Materials
Tech ID/UC Case
27517/2016-708-0
Related Cases
2016-708-0
- 国家/地区
- 美国






